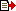
This mission will be implemented from the end of September to the middle of November, during which time the Tiangong-1 target vehicle and Shenzhou 8 spaceship will be launched in succession to carry out rendezvous and docking. The Long March 2F T1 rocket launching Tiangong-1 is scheduled to lift off during a launch window that extends from 21:16 to 21:31 (1316-1331 GMT; 8:16-8:31 a.m. CDT) on Sept. 29.

The main tasks of the Tiangong-1 spaceflight include: to provide a target vehicle for space rendezvous and docking experiments; to primarily establish a manned space test platform capable of long-term unmanned operation in space with temporary human attendance, and thus accumulate experiences for the development of a space station; to carry out space science experiments, space medical experiments and space technology experiments.
According to the schedule, Tiangong-1 will have two orbit maneuvers after launch before entering a 350 km (217 mile) near circular orbit and conducting in-orbit tests. Before the launch of Shenzhou 8, Tiangong-1 will descend to a 343 km (213 mile) near circular orbit waiting for rendezvous and docking.
Within two days of the launch of the unmanned Shenzhou 8, the first rendezvous and docking with Tiangong-1 will be performed and form a complex. After 12 days of flying joined as a complex, Shenzhou 8 will undock and perform a second rendezvous and docking. When that operation of the complex ends, the spaceship will return to the earth within one day.
Tiangong-1 will then ascend to an autonomous flight orbit and convert into long-term operation management mode waiting for the next rendezvous and docking.

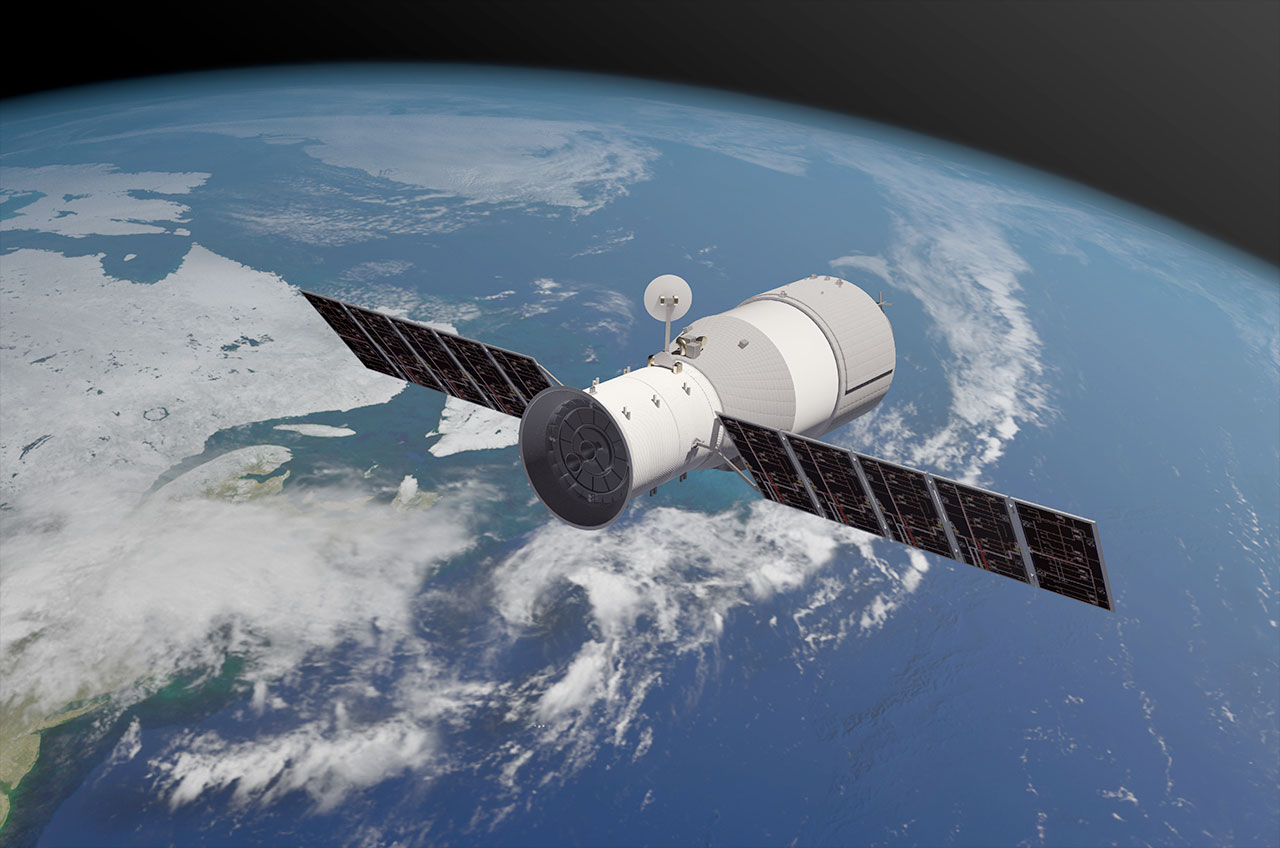
Tiangong-1 is a newly developed spacecraft with a total length of 10.4 meters (34 feet), maximum diameter of 3.35 meters (11 feet), liftoff mass of 8.5 tons, and its designed life span in orbit is two years. It consists of an experiment module and a resource module.
The effective volume of the experiment module is about 15 cubic meters which can satisfy three astronauts to work and live in it. A passive docking mechanism is installed in its front so as to enable docking with the spaceship. The resource module provides power and energy for the spaceflight.

The Long March 2F T1 rocket used to launch Tiangong-1 is a modified Long March 2F rocket. The escape system has been removed, a new type of fairing has been adopted and the structure of the boosters has been upgraded to increase their lift capability. The height of the rocket is 52 meters (170.6 feet), liftoff mass 493 tons and launch capability 8.6 tons.
The implementation of a space rendezvous and docking mission is the basis and premise for the construction of a Chinese manned space station.