 advertisements advertisements
|

|
Shuttle-flown solid rocket segments arrive in Florida for Artemis I SLS
June 15, 2020 — A solid rocket booster segment that helped launch the Hubble Space Telescope, send the space shuttle Endeavour on its maiden mission and return John Glenn to orbit has arrived back at NASA's Florida spaceport to lift off once again — this time as part of the first Space Launch System (SLS) rocket.
The steel cylinder, which will help form one of the two, five-segment motors to be mounted to the Artemis I SLS core stage, was among the hardware that was delivered by train to NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Friday (June 12). The segments' cross-country journey began seven days earlier at Northrop Grumman's facility in Promontory, Utah, where the hardware had been serviced and loaded with the solid propellant that will provide more than 75 percent of the initial thrust for the planned 2021 uncrewed launch.
The segments' arrival on the Florida East Coast railroad marked the first delivery of the booster hardware in just over a decade. The last shipment to the Kennedy Space Center in support of the space shuttle was on May 27, 2010.
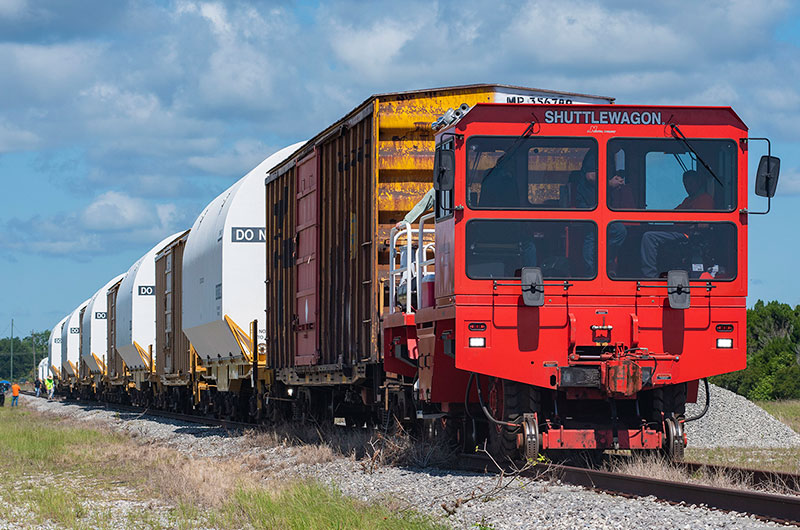
Loaded onto individual train cars, the 12 segments that arrived on Friday included the 10 fueled segments that will launch on the Artemis I mission and two inert common booster segments to be used as test hardware for Northrop Grumman's OmegA rocket.
The Artemis booster segments will be the first elements of the SLS rocket to be stacked on NASA's new mobile launcher inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). They will eventually be joined by the SLS core stage, interim cryogenic propulsion stage, Orion spacecraft and launch abort system before rolling out to Launch Complex 39B for the circumlunar mission.
The SLS is NASA's primary launch vehicle for its Artemis program, which has the goal of returning astronauts to the moon by 2024. The SLS will then be used to support establishing a sustained presence on the moon in preparation for sending the first humans to Mars.
"New technologies and material upgrades enable the boosters to meet the high performance demands of SLS, the most powerful rocket NASA has built to date," Charlie Precourt, vice president for propulsion systems at Northrop Grumman and a former NASA astronaut said in a statement. "Our technology will help propel the first woman and the next man to the moon."
All together, the Artemis I solid rocket booster segments previously helped launch 40 space shuttle missions dating back 30 years.
The oldest cylinder, which will fly as part of the booster mounted on the right side of the SLS core stage, first lifted off on the STS-31 mission with the Hubble Space Telescope on April 24, 1990. It was then used for six more shuttle flights, including Endeavour's debut on STS-49 in 1992 and STS-95 in 1998, which lifted off with Mercury astronaut and senator John Glenn as part of its crew.
Other notable missions that are part of the Artemis I boosters' legacy include: STS-71, which marked the first shuttle docking with the Russian space station Mir in 1995; STS-93, which deployed the Chandra X-ray Observatory and marked the first spaceflight commanded by a woman, Eileen Collins, in 1999; STS-114, the return to flight after the loss of the space shuttle Columbia in 2005; and STS-133, the final launch of the space shuttle Discovery in 2011.
The hardware also includes new components, including the two forward domes, two cylinders and four stiffeners.
The Artemis I mission will mark the final launch for all of the hardware as unlike during the space shuttle program, the solid rocket boosters will not be recovered after they splash down in the ocean due to budget constraints.
A schedule for stacking the booster segments has not yet been released. Though the mobile launcher stands ready and the modifications to Pad 39B have been completed, the Artemis I SLS core stage must first pass a series of "green run" engine tests at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi before it can join the mission's other components in Florida. |
|

The solid rocket booster segments for NASA's first Space Launch System (SLS) rocket arrived by train to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, June 12, 2020. (Northrop Grumman)

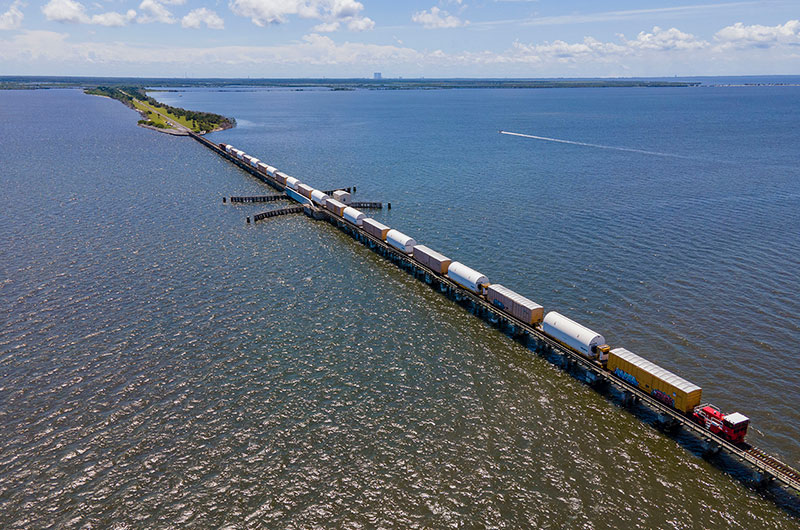
Marking the first such delivery in a decade, space shuttle-era solid rocket booster segments arrive at NASA's Kennedy Space Center for the Artemis I mission in 2021. (Northrop Grumman)

In addition to the fueled segments for Artemis I, two inert common booster segments for Northrop Grumman's OmegA rocket also arrived in Florida by train, riding on red cars. (Northrop Grumman) |
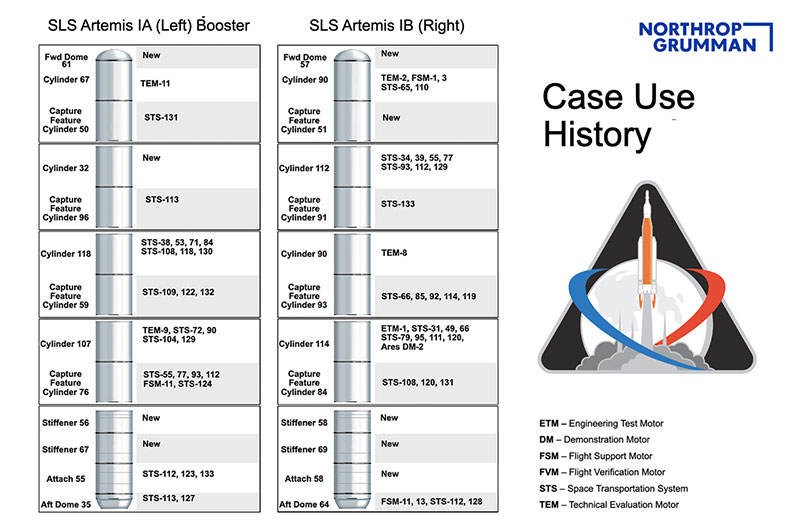
The solid rocket booster segments that will launch NASA's first Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis I mission previously flew on a total of 40 space shuttle missions, dating back 30 years. (Northrop Grumman/collectSPACE) |

The segments for NASA's Artemis I solid rocket boosters are moved onto Kennedy Space Center property on Monday, June 15, 2020. The Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), where the segments will be stacked for launch, can be seen on the horizon. (Northrop Grumman) |

The segments for NASA's Artemis I solid rocket boosters are moved onto Kennedy Space Center property on June 15, 2020. (Northrop Grumman) |
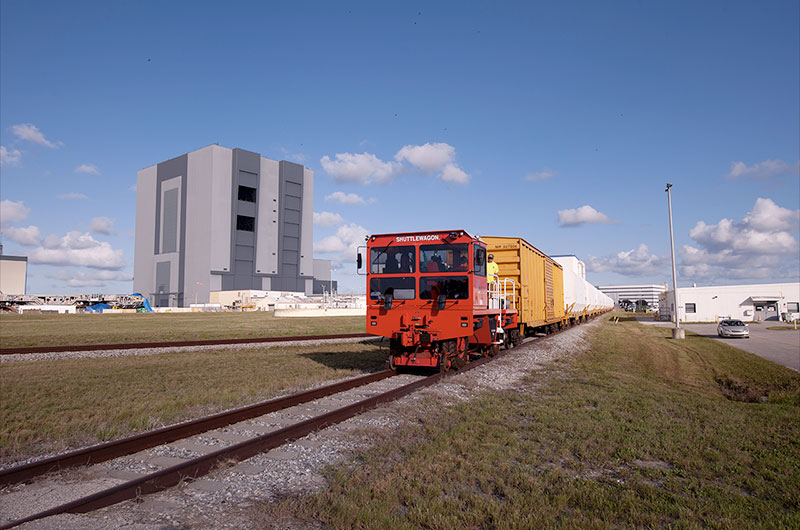

The segments for NASA's Artemis I solid rocket boosters are transported by rail near the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). (NASA/Kevin O'Connell) |
|

© collectSPACE. All rights reserved.
|
|

|

|
